Summary of the project
Ciliopathies are a large group of rare and severe genetic diseases caused by dysfunction of the primary cilium, a microtubule-based cell surface antenna that controls key signaling output required during development and tissue homeostasis. Cilium dysfunction leads to complex disorders with high genetic heterogeneity and overlapping phenotypes. Despite the broad clinical spectrum, chronic kidney disease (CKD) leading to end stage kidney disease (ESKD) is a common cause of morbidity across ciliopathies. Currently, the only available standard of care for CKD is based on dialysis and transplantation.
Renal ciliopathies represent a main cause of ESKD during childhood and despite the identification of more than 40 causative genes, it remains difficult to predict the severity of the disease as well as the risk of appearance (if not present at diagnosis) and the rate of progression of renal failure. TheRaCil therefore aims:
- To improve diagnosis and prognosis of at risk pediatric renal ciliopathy patients
- To implement therapeutic approaches aimed at targeting shared pathological pathways, at modifying mRNA targets of the causative or modifier genes by antisense oligonucleotides and by the repurposing of available molecules
These goals will be achieved through the federation of our unique databases of pediatric renal ciliopathies cases available across Europe, which will allow a better stratification of patients, the identification of modifier genes and markers of disease progression. Bioinformatics approaches will be used to integrate patients’ biological and genetic data as well as multi-omics and functional analyses from patients samples and preclinical models. These analyses should lead to the identification of shared targetable pathological pathways as well as of patients eligible for the identified new therapeutic approaches which will be evaluated in robust preclinical models
WP 1
Data integration and clustering for predictive signatures
Objectives :
- Integrate the data available at each site in a hybrid federated/centralized manner and define data exchange formats
- Deliver a common data model to the ciliopathy community
- Exploit state-of-the-art database infrastructure for subsequent biostatistical and bioinformatic analyses required in WP3
- Provide a disease model (pathways, drug targets, variants) through machine learning trained on these data
- Apply the above to a patient population to achieve relevant patient clustering and identify patients eligible to the trials designed in WP7
Lay summary :
The first aim of this work package is to integrate data about renal ciliopathies from all partners into a common database, containing patient symptoms, their brief genetic information, and information on the biological samples that are available for each patient. It will include comprehensive clinical data from over 3,700 patients from several countries.
This data, as well as additional data from DNA and RNA sequencing, for example, when available, will then be analyzed with biostatistics and machine learning to better understand the mechanisms of these diseases.
Next, algorithms will be developed to group patients according to their symptoms and biological data. They will allow more personalized treatment options for each group. They will also help us find undiagnosed patients through their electronic health records and identify those who could benefit from future clinical studies.
WP 2
Molecular signatures and mechanistic principles for classification and therapy
Objectives :
- Decipher the molecular signatures and disturbed signaling pathways in disease conditions and how they can be modified by therapeutic interventions
- Understand how therapeutic interventions modify the identified disturbed ciliopathy protein modules and the composition of primary cilia
- Investigate the effect of candidate therapies on individual renal cell populations, cell metabolism, and extracellular vesicle release
- Validate and select targetable pathways, disease modifiers and interventions for further preclinical studies
Lay summary :
In Work Package 2 we study the molecular and cellular changes that result from genetic variants in different pediatric ciliopathies that affect the kidneys. Research from the last 20 years has shown that cilia play a central role in this group of diseases. Cilia are antenna-like structures through which cells receive signals from their surroundings, and their functions in cells and tissues can be studied well in the lab. However, cilia regulate many different processes in cells, and it is still unclear which changes at the cellular level are actually crucial for kidney disease and thus would be the best targets for therapies.
This research will be done using basic science techniques on cultured cells, complex stem cell-derived 3D cell clusters called “organoids,” and animal models. We will use modern mass spectrometry methods to study the composition of cilia, combined with high-resolution microscopy, single-cell analysis of gene expression, and metabolomic analyses to investigate changes in cells and tissues in various diseases and their responses to interventions.
Our main aim is to obtain a sort of molecular fingerprint or signature of different types and stages of diseases. We believe this might provide a better starting point for understanding these conditions compared to solely genetic analyses since the same genetic change can lead to a wide range of symptoms of varying severity. In addition to precisely describing the diseases through these molecular signatures, we want to study how such signatures change with therapeutic interventions, contributing to future therapy strategies.
WP 3
Patient Eligibility to treatment : prognostic tools and biomarkers
Objectives :
- Identify biomarkers of kidney disease onset and progression
- Validate genetic modifiers of disease severity
- Generate a predictive model for clinical applications
Lay summary :
Background: For kidney conditions called renal ciliopathies, the usual tests for kidney function and protein in urine don’t tell us much about how the disease will progress. This work package’s goal is to create a tool that can predict early signs of nephronophthisis and foresee if the disease will worsen quickly. This way, we can enhance treatment options, keep an eye on how treatments are working, and catch potential issues early on.
Task 3.1: Identification of biomarkers of kidney disease
The first task is to take urine and blood samples from patients and healthy people and compare the components. This way we will try to identify new special markers, so called biomarkers that give us clues about the start of the disease and help us to foresee how one’s disease will progress.
Task 3.2: Development of a predictive tool
In the second task we will look at patients’ symptoms and their kidney function and try to find out how they are connected. Already known biomarkers will be analysed in patient urines from different disease stages. In addition, we will look at biomarkers that have been identified in animal models to check if they are helpful in gaining new information in human disease.
Task 3.3: Identification of genetic modifiers
Certain changes in the DNA, so called genetic modifiers in patients with NPHP1 disease are known to give us information about when the kidney function will start to go bad. Here, we will see if those modifiers can also give us information about the kidney function in other ciliopathies. Also, we will focus on patients where the kidney function goes bad really early or really late and check for genetic modifiers using a method that analyses the entire patient DNA (whole-genome sequencing). Finally, we will see in what ways the newly identified modifiers affect the process by which the information encoded in a gene is turned into a function using a method called RNA sequencing.
We will integrate gained results into work package 1 to design a model that can predict the course of a disease and to help identify patients eligible for clinical trials.
WP 4
Advanced Therapeutic strategies suitable for clinical use
Objectives :
- Prioritize advanced lead molecules in robust models recapitulating NPH/ARPKD clinical features
- Complete the pharmacological target product profile assessment of the most advanced EP2 agonist
- Improve therapeutic modalities with ASO specifically for use in renal ciliopathies
Lay summary :
Several teams from the consortium have obtained encouraging results concerning potential treatments for pediatric renal ciliopathies (nephronophtisis (NPH) and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)), using different approaches (drug repurposing and RNA-based therapies). This work package aims at 1) optimizing and validating these first treatment leads 2) exploiting the results from WP1, 2 and 3 to find new leads 3) setting up approaches for screening small molecules to target these and other renal ciliopathies (Bardet-Biedl Syndrome and ARPKD).
Task 4.1: Identification and Validation of therapeutic candidate compounds.
The potential treatments that have already been identified will be tested in other genetic contexts in the different cellular and animal models generated by the consortium. New molecules/drugs targeting dysfunctional cellular mechanisms identified in WP1 will be tested in a similar way. Their efficacy will be evaluated by using disease markers identified in WP2 and WP3.
Task 4.2: Phenotypic drug screening in iPSC-derived kidney organoid model of ARPKD
By quantifying the cysts that develop in renal organoïds obtained from ARPKD patient cells, it will be possible to set up a screen to identify molecules that could reduce their size or number. The molecules identified will be characterized and tested in the different animal models available in the consortium.
Task 4.3: Development and Optimization of candidate therapeutic compound for NPH
A molecule that is stimulating the prostaglandin receptors has shown very promising effects on patient cells and in a mouse model of nephronophtisis. This molecule, and others with the same properties that will be selected by the consortium, will be characterized from a pharmacological point of view (dosage, toxicity) and in terms of their efficacy in different models.
Task 4.4: Extend the potential therapeutic modalities with ASOs applicable in renal ciliopathies
In addition to the approaches using classical pharmacological molecules, a team in the consortium develops antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) in the context of nephronophtisis. ASOs allow to target the products of genes (messenger RNA) directly in kidney cells and to cut some of them to eliminate the mutation causing the disease. A mouse model mimicking a human mutation has been generated and will be used for testing the ASOs and validating their effects on kidney disease.
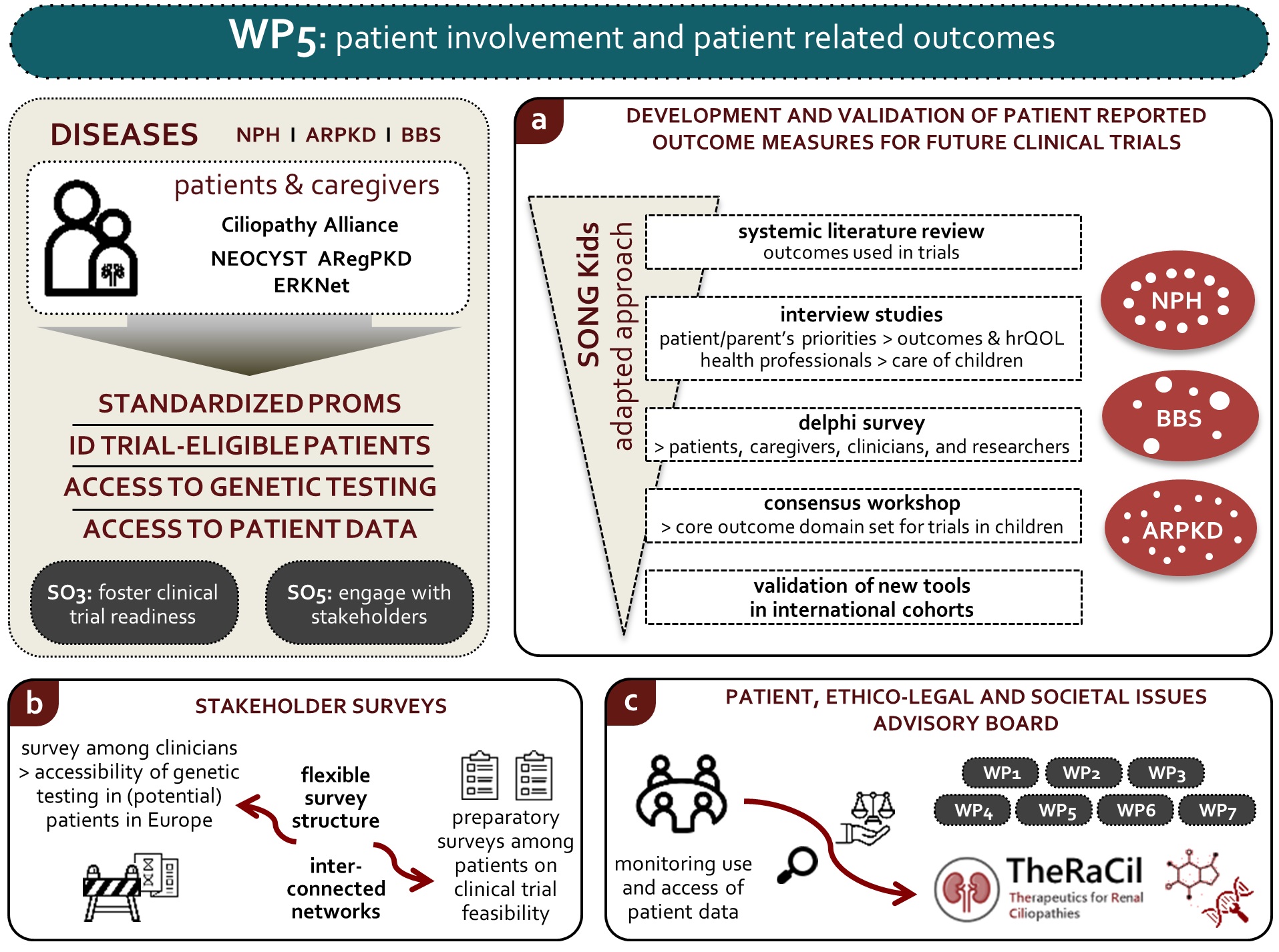
WP 5
Patient involvement and patient Centered Outcomes
Objectives :
- Identify, define and prioritize standardized PROMs for future clinical trials in ARPKD, NPH and BBS
- Improve identification of trial-eligible renal ciliopathy patients by assessing access and barriers to genetic testing
- Monitor the use and access of patients’ data
Lay summary :
Background: Unclear diagnostics, uncertainty of how the disease will progress, facing an illness with an unclear start and extent, as well as inconsistent management are great concerns of patients with cystic kidney disease. Early onset cystic kidney disease has a major impact on the intellectual development, psychosocial integration and family life. This applies even more when other health problems like reduced vision, long-lasting liver disease or mental disabilities go along with kidney failure. The focus of this work package is to address the interests and needs of affected individuals. We aim to capture and reflect the patients’ limitations in everyday life and their personal perception of the disease.
Task 5.1: In order to secure interests from drug companies to make a new medication available to patients it is necessary to follow a set of rules set by regulatory authorities. One-step is to include patient ideas into benefit-risk assessments. Opinions that reflect honest benefits from a patient view are very important, as rare disease therapies should be established to benefit patients and not just treat their disease. The main objective of this task is the recording of standardized patient opinions; so-called patient related outcome measures (PROMs). The purpose of PROMs is to put patients, their families and caregivers in the centre of decisions concerning the most important measures in the plan of care, rather than leaving decisions exclusively to the doctors.
Task 5.2: Over the past years, genetic testing for patients with suspected hereditary kidney disease has become technically feasible. However, there are barriers across Europe that prevent patients from accessing and benefiting from genetic services in (pediatric) nephrology. To improve the accessibility and quality of care -including access to clinical trials and ultimately treatment- for these patients, we aim to identify these barriers.
By identifying the barriers for genetic testing of patients with ciliopathies and suspected hereditary kidney disease in general, our survey can show specific points of improvement to enhance the accessibility of genetic testing in this patient group. The report will be useful and exploited within the rare disease community. Also, it will provide input to European Union and national policies on the access to genetic testing. The results will be used within TheRaCiL to help in better identifying patients who are eligible for potential treatments and in selecting suitable trial centres. Furthermore, the results will be widely shared to ensure fewer patients remain undiagnosed uncounseled and ultimately untreated with the treatments that we aim to develop.
Task 5.3: The main objective of this task is to establish an advisory board that addresses ethical, legal and social issues: the PELSI (Patient, EthicoLegal and Societal Issues) Advisory Board. The PELSI board will include representatives from international patient advocacy groups and parents of children with cystic kidney disease. The board will make sure that patient data is protected by monitoring how the data is being used and accessed.
WP 6
Coordination and Management
Objectives :
- Monitor the project progress in terms of technical and administrative coordination among all partners
- Provide timely and efficient organizational and financial coordination to meet contractual requirements and commitments.
WP 7
Dissemination, communication and exploitation
Objectives :
- Engage and disseminate the results of the project widely to stakeholders
- Communicate about the project to the general public and potential stakeholders
- Align knowledge and results arising from the project with partner interests, market and regulatory needs and manage intellectual property to produce plans and agreements for post-project exploitation
WP 8
Ethics Requirements
Objectives :
- Give advice and guidance to all partners in order to ensure protection of the rights and interests of all those affected by the research
- Give advice and guidance to all partners in order to ensure respect for fundamental EU values and human rights
- Verify compliance with existing regulations